Creatinine Clearance GFR Calculator
Creatinine Clearance (GFR) Calculator
Creatinine Clearance Formula, Cockcroft-Gault equation?
The most commonly used formula to calculate creatinine clearance is the Cockcroft-Gault equation. This equation estimates creatinine clearance based on a person’s age, weight, serum creatinine level, and gender. The formula is as follows:
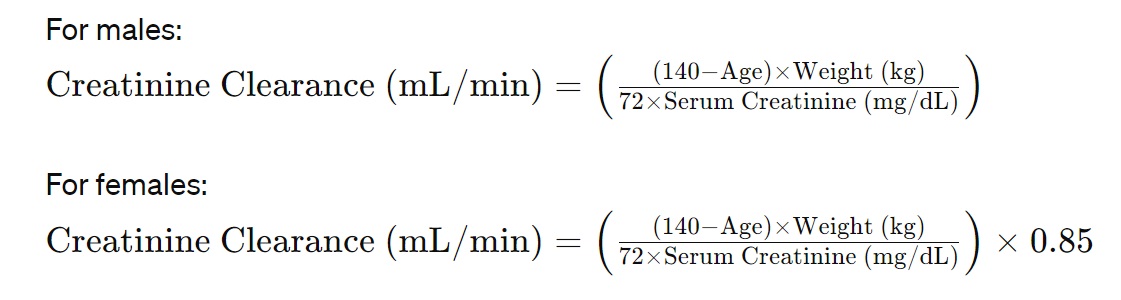
- Age is the person’s age in years.
- Weight is the person’s weight in kilograms.
- Serum Creatinine is the person’s serum creatinine level in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL).
- The factor 0.85 is used for females to adjust for the lower muscle mass compared to males.
This equation provides an estimation of creatinine clearance and may not be as accurate in certain populations, such as those with extreme muscle mass, amputations, or significant weight fluctuations.
Creatinine clearance may also be affected by factors such as diet, medications, and hydration status. Our calculator provided an estimate number and may not be the most accurate one. Source
What is Creatinine Clearance?
Creatinine clearance is a measure of how effectively the kidneys filter waste products, specifically creatinine, from the blood. Creatinine is a waste product generated by the muscles from the breakdown of a compound called creatine phosphate, which is used by the muscles for energy.
The kidneys filter creatinine from the blood and excrete it into the urine. Creatinine clearance is used as an indicator of kidney function, particularly the glomerular filtration rate (GFR), which represents the rate at which the kidneys filter blood.
Creatinine Clearance Test?
The creatinine clearance test is a diagnostic test used to measure how efficiently the kidneys are filtering waste products, specifically creatinine, from the blood. Creatinine is a waste product generated by the muscles from the breakdown of a compound called creatine phosphate, which is used by the muscles for energy.
During the test, a 24-hour urine sample is collected, along with a blood sample. The urine sample measures the amount of creatinine excreted by the kidneys over a 24-hour period, while the blood sample measures the amount of creatinine present in the bloodstream.
The result of the creatinine clearance test is expressed in milliliters per minute (mL/min) and provides an estimate of the glomerular filtration rate (GFR), which represents the rate at which the kidneys filter blood.
This test is commonly used to assess kidney function, diagnose kidney diseases, monitor the progression of kidney disorders, and adjust medication dosages, particularly drugs that are eliminated by the kidneys.
Creatinine Clearance Normal Range
The normal range for creatinine clearance can vary depending on factors such as age, sex, and muscle mass. Generally, normal creatinine clearance values for adults range from approximately 90 to 140 milliliters per minute (mL/min). However, laboratories may have slightly different reference ranges.
Abnormal creatinine clearance values may indicate underlying kidney dysfunction or disease. Values below the normal range may suggest impaired kidney function, while values above the normal range may indicate hyperfiltration, which can occur in conditions such as diabetes or early kidney disease stages.
Creatinine Clearance normal range chart:
| Gender | Normal Creatinine Clearance Range (mL/min) | Abnormal Creatinine Clearance Range (mL/min) |
|---|---|---|
| Male | 90-140 | Below 90 (impaired kidney function) |
| Female | 85-125* | Below 85 (impaired kidney function) |
*Note: The normal range for females is typically slightly lower than that for males due to differences in muscle mass.
Explanation:
Normal Creatinine Clearance Range:
- For males, the normal range of creatinine clearance is typically between 90 to 140 mL/min.
- For females, the normal range is slightly lower, typically between 85 to 125 mL/min, due to differences in muscle mass compared to males.
Abnormal Creatinine Clearance Range:
- Creatinine clearance values below the normal range indicate impaired kidney function. For both males and females, values below 90 mL/min are considered abnormal.
- It’s important to note that values may vary depending on individual factors such as age, muscle mass, and medical history.
What is normal creatinine clearance levels?
Normal creatinine clearance rates can vary by age, sex, and body size, but in general, they are used as an indicator of kidney function. Creatinine clearance is measured in milliliters per minute (mL/min) and is adjusted for body surface area. Here’s a general guideline:
- Adult men: Typically, a normal creatinine clearance rate is about 95 to 135 mL/min per 1.73 m² of body surface area.
- Adult women: Usually, a bit lower, around 85 to 125 mL/min per 1.73 m² of body surface area.
What creatinine level indicates kidney failure?
Creatinine levels in the blood are a key indicator of kidney function, and elevated levels can suggest kidney damage or failure. However, the exact level of creatinine that indicates kidney failure can vary based on several factors, including age, gender, muscle mass, and the lab’s specific reference ranges. Generally, creatinine levels are measured in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) in the United States and in micromoles per liter (μmol/L) in many other countries. Here’s a basic guideline:
Normal ranges: Typically, normal blood creatinine levels are approximately 0.6 to 1.2 mg/dL for men and 0.5 to 1.1 mg/dL for women. These ranges can vary slightly between labs.
Indication of kidney failure: A creatinine level higher than the normal range for adults may indicate kidney damage or dysfunction. In the context of kidney failure (end-stage renal disease), creatinine levels are often significantly elevated, often above 4.0 mg/dL (353.6 μmol/L), but the specific level can vary widely depending on the individual.
How to compute creatinine clearance?
Creatinine clearance (CrCl) is calculated to estimate the glomerular filtration rate (GFR), which reflects the kidney’s function. The most commonly used method to calculate creatinine clearance is the Cockcroft-Gault formula, which considers a person’s age, body weight, sex, and serum creatinine level. It’s important to note that this formula provides an estimate of creatinine clearance adjusted for body surface area, not the actual GFR.
Cockcroft-Gault Formula:

For women, the result of the calculation for men is multiplied by 0.85, reflecting the general difference in muscle mass between sexes.
- Age is in years.
- Weight is in kilograms.
- Serum creatinine is in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL).
This formula is widely used in clinical settings to adjust dosages of medications that are primarily excreted by the kidneys and to evaluate patients’ kidney function. However, it has its limitations, especially in those with very high or very low body mass, the elderly, and those with unstable kidney function.
Common Questions & Answers
Is creatinine clearance the same as eGFR?
Creatinine clearance and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) are related but not the same. Creatinine clearance is a measure of how well creatinine is being removed from the blood by the kidneys and usually involves a urine collection to measure creatinine. eGFR, on the other hand, is a calculation based on blood serum creatinine levels, age, sex, and race to estimate how much blood passes through the glomeruli each minute.
Both measures give an indication of kidney function but use different methods and calculations.
What creatinine level needs dialysis?
The need for dialysis does not depend solely on serum creatinine levels but rather on the overall clinical picture, including symptoms and other measures of kidney function like eGFR.
Typically, dialysis is considered when eGFR drops below 15 mL/min/1.73 m² or in the presence of life-threatening symptoms of kidney failure, regardless of the precise creatinine level.
What creatinine level is dangerous?
A serum creatinine level significantly higher than the normal range (e.g., greater than 2.0 mg/dL for most adults) can be concerning and warrants further evaluation. However, what’s considered dangerous varies by individual and needs to be interpreted in context with other clinical findings.
What is a good creatinine clearance?
A good creatinine clearance rate is generally considered to be within the range of 95 to 135 mL/min for men and 85 to 125 mL/min for women, adjusted for body surface area. These ranges can vary based on age and muscle mass.
Can creatinine levels go back to normal?
Yes, if the increase in creatinine levels is due to a reversible cause such as dehydration or medication side effect, addressing the cause can return the levels to normal.
Can creatinine levels fluctuate?
Yes, creatinine levels can fluctuate based on hydration status, dietary intake, muscle mass changes, and use of certain medications.
Can creatinine levels be lowered?
Creatinine levels can be lowered by treating the underlying cause of the kidney dysfunction, such as controlling blood pressure, managing diabetes, and avoiding nephrotoxic drugs. Lifestyle changes, such as a healthier diet and proper hydration, can also help.
What creatinine level to stop metformin?
Metformin is typically contraindicated or used with caution in patients with reduced kidney function, often advised when the creatinine levels exceed 1.5 mg/dL for men and 1.4 mg/dL for women, or if eGFR falls below 30 mL/min/1.73 m², although recommendations can vary.
What creatinine level is stage 3?
Stage 3 chronic kidney disease (CKD) is defined by an eGFR of 30 to 59 mL/min/1.73 m², not directly by creatinine levels, as eGFR is a more accurate measure of kidney function stages.
Are creatinine clearance and GFR the same?
They are related measures of kidney function but not identical. GFR is a more comprehensive estimate of kidney filtering capacity, while creatinine clearance specifically measures the rate at which creatinine is cleared from the blood by the kidneys.
Why does creatinine level increase?
Creatinine levels can increase due to factors that impair kidney function, including dehydration, renal artery stenosis, diabetes, hypertension, and drugs that are toxic to the kidneys.
Muscle mass increases or high meat intake can also cause higher creatinine levels.
Other Similar Calculators
