Morphine Equivalent Calculator - Opioid Dose Conversion
Morphine Equivalent Calculator
How to Use Morphine Equivalent Calculator
Opioid Selection:
Users can select the opioid from a dropdown menu. Supported opioids include:
Morphine
Oxycodone
Hydrocodone
Fentanyl (mcg/hr)
Hydromorphone (Dilaudid)
Codeine
Methadone
Tramadol
Dose Input (mg/dose):
Users can enter the dose of the selected opioid in milligrams per dose (mg/dose).
Doses Per Day:
Users can specify the number of doses taken per day.
Morphine Equivalent Dose (MED) Calculation:
The calculator uses standard conversion factors to convert the total daily dose of the selected opioid into an equivalent dose of morphine.
Result Display:
The calculator displays the following results:
Morphine Equivalent Dose (MED) in mg/day.
Selected opioid.
Dose in mg/dose.
Number of doses per day.
Total daily dose in mg/day.
Morphine Equivalent Dose Calculator is a tool designed to help healthcare professionals and patients convert doses of various opioids into an equivalent dose of morphine.
This is useful for comparing the potency of different opioids and ensuring safe prescribing practices.
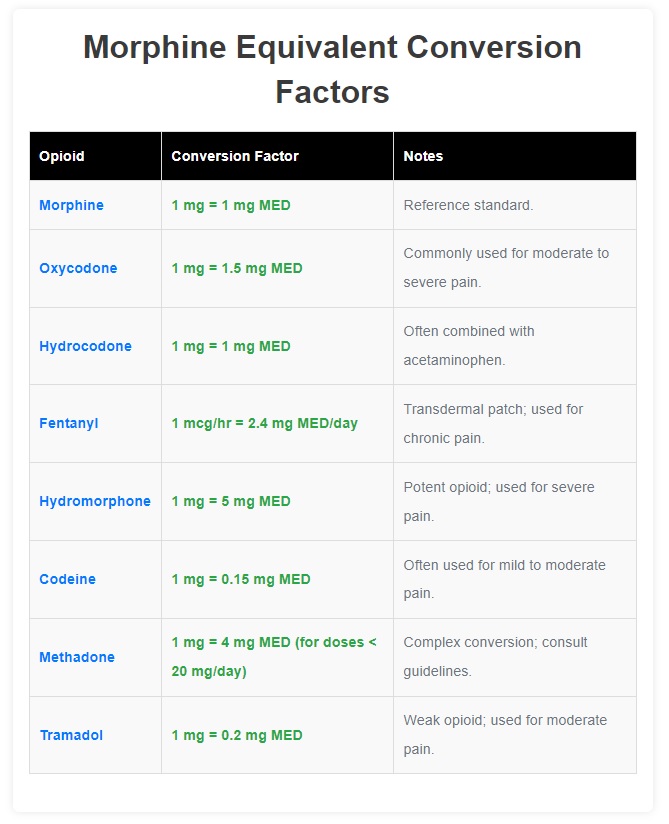
Key Notes:
Morphine is the reference standard, with a conversion factor of 1:1.
Fentanyl doses are entered in mcg/hr and converted to mg/day of morphine equivalent.
Methadone conversion is complex and depends on the dose. For doses < 20 mg/day, the conversion factor is 1 mg = 4 mg MED.
Always consult clinical guidelines and consider patient-specific factors (e.g., renal/hepatic function) when converting opioid doses.
Some common keywords related to Morphine Equivalent Dose Calculator:
Morphine Equivalent Dose Calculator
Opioid Conversion Calculator
MED Calculator
Opioid Equianalgesic Calculator
Morphine Milligram Equivalent (MME) Calculator
Opioid Dose Conversion Tool
Pain Management Calculator
Opioid Equivalence Chart
Morphine Equivalent Dose Chart
Opioid Rotation Calculator
MME Conversion Tool
Analgesic Dose Calculator
Opioid Tolerance Calculator
Pain Medication Conversion Calculator
Equianalgesic Dose Calculator
Opioid Dose Equivalence
Morphine Equivalent Dose Formula
Opioid Conversion Chart
Chronic Pain Opioid Calculator
Opioid Risk Assessment Tool
Common Questions and Answers
What is a Morphine Equivalent Dose (MED) Calculator?
A MED calculator is a tool used to convert the dose of one opioid to an equivalent dose of morphine. It helps standardize opioid doses for comparison, ensuring safe and effective pain management.
How do I calculate morphine equivalent doses?
Morphine equivalent doses are calculated using equianalgesic conversion factors. For example, if 10 mg of oral hydromorphone is equivalent to 30 mg of oral morphine, the conversion factor is 1:3. Multiply the dose of the current opioid by its conversion factor to get the morphine equivalent dose.
Why is it important to calculate morphine equivalents for opioids?
Calculating morphine equivalents ensures safe dosing, prevents overdose, and allows healthcare providers to compare the potency of different opioids. It is especially important when rotating or switching opioids.
How do I convert one opioid to another using a MED calculator?
First, convert the current opioid dose to its morphine equivalent using the calculator. Then, use the conversion factor for the target opioid to find the equivalent dose. For example, to convert morphine to oxycodone, divide the morphine dose by 1.5 (since 1 mg of oxycodone ≈ 1.5 mg of morphine).
What is the formula for calculating morphine milligram equivalents (MME)?
The formula is:
MME = Dose of Opioid (mg) × Conversion Factor
For example, 20 mg of oxycodone × 1.5 (conversion factor) = 30 MME.
Can I use a MED calculator for opioid rotation or switching?
Yes, a MED calculator is essential for opioid rotation. It ensures the new opioid dose is equivalent to the previous one, minimizing the risk of under- or over-dosing.
How accurate are morphine equivalent dose calculators?
MED calculators are generally accurate but should be used cautiously. Individual patient factors (e.g., tolerance, metabolism, and comorbidities) can affect the accuracy, so clinical judgment is crucial.
What are the risks of incorrect opioid dose conversion?
Incorrect conversions can lead to overdose (respiratory depression, sedation) or under-dosing (inadequate pain relief). Always double-check calculations and consider patient-specific factors.
How do I calculate MME for chronic pain management?
Calculate the total daily dose of the opioid, then multiply by its conversion factor to get the MME. For example, if a patient takes 40 mg of oxycodone daily:
40 mg × 1.5 = 60 MME/day.
Is there a standard conversion factor for opioids to morphine equivalents?
Yes, standard conversion factors are available (e.g., 1 mg of oral hydromorphone = 4 mg of oral morphine). However, these factors may vary slightly depending on the source.
How do I use an opioid conversion chart with a MED calculator?
An opioid conversion chart provides equianalgesic ratios. Use the chart to find the conversion factor for the opioid, then input the dose into the MED calculator to determine the morphine equivalent.
What is the difference between MED and MME?
MED refers to the equivalent dose of morphine, while MME (Morphine Milligram Equivalent) quantifies the total opioid dose in terms of morphine’s potency. Both terms are often used interchangeably.
Can a MED calculator help reduce opioid overdose risk?
Yes, by ensuring accurate dose conversions, a MED calculator helps prevent accidental overdose, especially when rotating opioids or prescribing high doses.
How do I calculate morphine equivalents for fentanyl patches?
Fentanyl patches are calculated differently due to their transdermal delivery. For example, a 25 mcg/hr fentanyl patch is approximately equivalent to 90 mg of oral morphine per day.
What are the limitations of a morphine equivalent dose calculator?
Limitations include:
Not accounting for individual patient factors (e.g., tolerance, metabolism).
Variability in conversion factors between sources.
Not suitable for mixed agonist-antagonist opioids (e.g., buprenorphine).
How do I adjust opioid doses for patients with renal or hepatic impairment?
For patients with renal or hepatic impairment, reduce the calculated MED by 25-50% and titrate slowly to avoid toxicity. Consult clinical guidelines for specific recommendations.
Are there free online tools for calculating morphine equivalent doses?
Yes, many free online tools and apps are available, such as the CDC Opioid Guideline Mobile App or GlobalRPH Opioid Converter.
How do I interpret results from a MED calculator?
The result represents the equivalent dose of morphine. Use this to guide opioid rotation, assess overdose risk, or ensure compliance with prescribing guidelines (e.g., CDC recommends avoiding doses >90 MME/day).
What are the guidelines for using a MED calculator in clinical practice?
Guidelines include:
Always verify calculations.
Consider patient-specific factors (e.g., age, comorbidities).
Use the lowest effective dose to minimize risks.
Follow CDC or local prescribing guidelines.
How do I calculate morphine equivalents for partial agonists like buprenorphine?
Partial agonists like buprenorphine have complex conversions and are not directly comparable to full agonists like morphine. Use specialized conversion tables or consult a pain management specialist.
Morphine Equivalent Conversions Calculations
Question 1: A patient is prescribed 30 mg of oral oxycodone daily for pain management. What is the equivalent dose in morphine milligram equivalents (MME)?
Answer:
- Identify the conversion factor for oxycodone to morphine:
- 1 mg of oral oxycodone = 1.5 mg of oral morphine.
- Calculate the MME:
- Multiply the oxycodone dose by the conversion factor.
- 30 mg oxycodone × 1.5 = 45 MME.
- Final Answer:
- 30 mg of oral oxycodone is equivalent to 45 MME.
Question 2: A patient is using a 50 mcg/hr fentanyl patch. What is the equivalent daily dose in morphine milligram equivalents (MME)?
Answer:
- Identify the conversion factor for fentanyl patches to oral morphine:
- 1 mcg/hr of transdermal fentanyl ≈ 2.4 mg of oral morphine per day.
- Calculate the MME:
- Multiply the fentanyl patch strength by the conversion factor.
- 50 mcg/hr × 2.4 = 120 mg of oral morphine per day.
- Final Answer:
- A 50 mcg/hr fentanyl patch is equivalent to 120 MME per day.
